By: Lawrence Harte
There are concerns that unlicensed WISP systems may not be able to provide reliable broadband Internet services. WISP system owners fear that users may experience outages or poor connections. Regulators and investors may not provide grants or funding and this may lead manufacturers to stop producing unlicensed radio systems. Unlicensed wireless technologies and systems have evolved enabling reliable connections and there are many multi-gigabit unlicensed wireless systems that have been in use since the early 2000s.
Wireless regulations define the frequencies, RF power levels, authorized services and who can use them. Licenced wireless regulations give exclusive rights to specific companies to provide defined types of services. Unlicensed wireless regulations define how multiple users can co-exist on a shared basis.
Unlicensed wireless technologies have evolved and continue to improve providing highly efficient and reliable connections. Shared communications systems such as WiFi, Bluetooth and the Internet allow connections to co-exist while providing reliable and cost-effective communication services. Unlicensed systems can be monitored and adapted to provide reliable communication services.
Unlicensed Wireless Technologies
Unlicensed radio system technologies have evolved and continue to improve enabling faster and more reliable services. Key wireless unlicensed technologies include RF power control, advanced modulation, channel coding, interference avoidance, transmission beamforming and multiple transmission signal path combining.
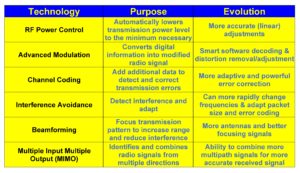
Figure 1, List of Unlicensed Wireless Technologies & Benefits
RF Power Control
RF power control is used to automatically lower transmission power level to the minimum necessary to communicate. This reduces the transmitted power, increases battery life and lowers interference to other users. RF amplifier technology has become more efficient (better conversion) and is more accurate (linear) enabling faster and more precise power control.
Advanced Modulation
Modulation is the process of adding information to a radio signal. Modulation can be done by amplitude, frequency and/or phase changes. Modulation technology has improved allowing smaller changes (shifts) to the transmitted signal allowing for more data to be converted (faster data rates). Modulator conversions may be done by software which has evolved to detect and adjust for distortions (interference). This increases the data rate while reducing the effects of interference.
Channel Coding
Channel coding is the adding of error detection and correction data to the information signal (voice or data). Error correction types and conversion have become more adaptive and provide more effective error correction increasing reliability and resistance to interference.
Interference Avoidance
Interference avoidance detects unwanted signals and uses this information to change frequencies and/or modify transmission packet formats. Interference avoidance processes have evolved to use adaptive frequency changing patterns and more rapid packet size and error coding options.
Transmission Beamforming
Beamforming is a radio signal process that creates a focused transmission pattern (a radio beam) which increases transmission range and reduces the interference to others. It is similar to using a flashlight to illuminate a small area. A low power light bulb can be focused to a spot at a far distance while not leaking light on either side of the beam. Radio beamforming can be done by electronically controlling signals to multiple antennas that transmit slightly delayed versions of their radio signals. This can focus and direct (steer) the transmission beam (pattern) in specific directions.
Multiple Transmission Path Combining
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) is a process that identifies and combines radio signals from multiple directions. Radio signals from a transmitter can travel through different paths to the receiver. Some signals may bounce off walls or objects and be received slightly delayed from the signal that travels directly from the transmitter to receiver. MIMO processing can identify and combine the effects of the multiple signals to create a stronger and more accurate received signal. MIMO systems have evolved to be able to combine radio signals from more travel paths.
Reliable Unlicensed Communication Systems
Many WISP systems have been providing commercial reliable broadband services on unlicensed frequencies since the early 2000s. Some started by offering wireless Internet services using standard WiFi technology and equipment in highly congested frequencies (900 MHz and 2.4 GHz).
Unlicensed WiFi systems can provide almost 1 Gbps of data transmission (WiFi 6). Managed unlicensed WiFi services are available in many airports, hotels and other venues that offer basic access and can charge for higher speed and more reliable managed connections. WiFi services are used on aircraft where hundreds of people simultaneously stream multi-megabit digital video signals in a very small area.
Bluetooth is a very short range unlicensed system that can allow dozens of devices to operate in close proximity with each other. Bluetooth devices are used in key applications such as police, EMS and other mission critical public safety applications. Bluetooth has many types of channel coding for different types of services. For example, a lot of error protection is added for very important services such as live video and low amounts of coding is used for flexible services such as audio.
The Internet is probably the best example of a highly reliable unlicensed communication system.
The Internet dynamically routes packets towards their destination through independent nodes that dynamically change their transmission processes. Internet packet transmission processes (protocols) have been developed which can mix, manage and verify packet delivery for many types of services. Unmanaged packet losses due to congestion in the Internet is expected because it indicates that there is no excess capacity (overbuilding).
Managing Unlicensed WISP System Reliability
Wireless systems and users can use multiple tools to monitor transmission data speed, packet delays (latency), errors and other criteria to detect and adjust systems to provide reliable and guaranteed performance.
 Lawrence Harte is a wireless communication and media expert. He has written 131+ books as of 2023 (30+ on wireless) and is the senior editor of Wireless Dictionary (wirelessdictionary.com). Mr. Harte has designed, installed and tested RF communication systems. He was a voting member of the TIA Industry standards committees where he reviewed and created digital mobile radio industry specifications. Mr. Harte has been a speaker at 110+ wireless industry events. He created and presented the 3 hour New RF Technologies course at IWCE conferences for 10+ years. Mr. Harte is the inventor of multiple patents on mobile system radio signaling.
Lawrence Harte is a wireless communication and media expert. He has written 131+ books as of 2023 (30+ on wireless) and is the senior editor of Wireless Dictionary (wirelessdictionary.com). Mr. Harte has designed, installed and tested RF communication systems. He was a voting member of the TIA Industry standards committees where he reviewed and created digital mobile radio industry specifications. Mr. Harte has been a speaker at 110+ wireless industry events. He created and presented the 3 hour New RF Technologies course at IWCE conferences for 10+ years. Mr. Harte is the inventor of multiple patents on mobile system radio signaling.